The black rat (scientific name: Rattus rattus) is a common arboreal long-tailed rat. It is the second of the most widespread species of rat in the world behind the brown (Norway) rat. In urban areas the black rats reside on the upper floors, attic and roof as they are nice climbers. Because of this habit they have been given the common name “roof rats”. They are also called the house rats, ship rats, Alexandrine rats, or old English rats. In fact, the black rats migrated from tropical Asia, and spread throughout Europe in Roman times. Thus, they did not originally come from England and Europe.
Habitat of black rats
Nowadays, the arboreal roof rats inhabit forests and disturbed areas in and near human settlements throughout the world. In fact, the black rats prefer regions with warmer climate and they are less resistant to weather extremes. However, they have been supplanted by the burrowing Norway rats in cooler urban areas.

Black rats are able to adapt to a wide range of habitats. In the forests, they live in trees, rocks, and cliffs. The roof rats also inhabit rural areas, they dwell in fruit trees, barns, warehouses, livestock yards, and crop fields.
Nesting and breeding activity
Black (roof) rats make spherical nests of shredded material, including leaves, sticks, other vegetation and plant materials, wires, ropes and cloth. They nest inside the wall cavities, false ceilings, in and behind lumber and boxes in the attic. In the wild, they occupy cavities and dens located in trees, soil and rocks. In the absence of trees, the roof rats are able to burrow into the ground.
The black rats can produce up to 8 babies four-five times a year. On average, their litters can number 5-7 young rats. The gestation period lasts 23-24 days.
Diet of roof rats
The black (roof) rats are generalist omnivores and eat a great variety of foods, such as stems, leaves, flowers, nuts, seeds, vegetables, fruit. Moreover, they feed on fungi, lizards, mice, birds, snails, insects and eggs. Thus, they destroy natural bird and animal habitats.

The black rats attack farms and eat agricultural-based crops, including coconuts, coffee beans, oranges, cereals, sugar cane, and cocoa. They may consume food provided for goats, horses, cows, swine, hens, and pets in livestock yards. In contrast to the brown rats, the roof rats need meal high in water content.
The roof rat mainly forages after sunset. If they can’t eat the found food immediately, they will look for a place to carry and tuck away to eat at a later time.
How the roof rats look like
Typical adult roof rats are smaller than brown ones. They are from 5 to 7 inches long. The roof rats exhibit several color forms. In fact, they have scraggly coats of black to light brown fur with lighter undersides.
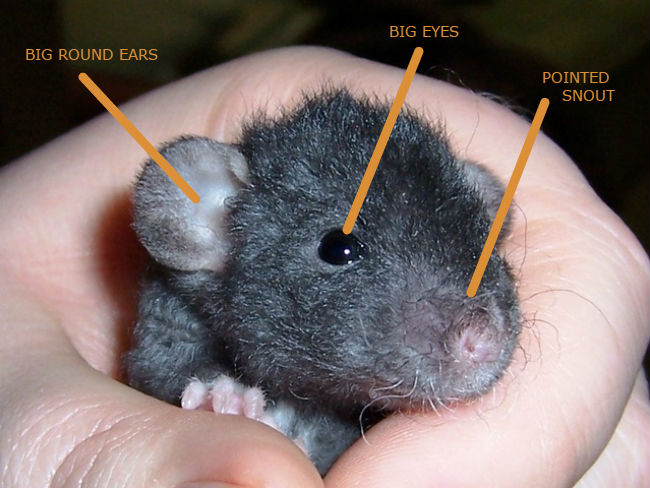
Their tails are hairless and longer than the rest of the body up to 8 inches in length. Moreover, a black rat weighs on average 4 – 12 oz, depending on its subspecies. They have big eyes and ears, a pointed snout and slender body shape.
Black rat feces
Roof rat droppings are pointed on both ends. They are black in color, shiny. They are 0.5 inches long.
Are roof rats dangerous to humans?
Black (roof) rats have an ability to hold so many infectious bacteria in their blood. Thus, they are more hazardous vectors of diseases than brown (Norway) rats. Roof rats were responsible for carrying the plague into Europe. They served as plague reservoirs, from which bacteria and infections spread through trade routes. The roof rats carry pathogens of Weil’s disease, typhus, trichinosis and toxoplasmosis as well.
Indeed, the change from wooden structures and thatched roofs to bricked and tiled buildings in settlements reduced the number of the black rat infestations indoors. However, if you have found the signs of their presence, hire a professional rat exterminator or kill the roof rats by yourself.
Leave a Reply